Carbon Monoxide observed by Sentinel-5p TROPOMI
Short description
Carbon monoxide (CO) is an important atmospheric trace gas for our understanding of tropospheric chemistry. In certain urban areas, it is a major atmospheric pollutant. Main sources of CO are combustion of fossil fuels, biomass burning, and atmospheric oxidation of methane and other hydrocarbons. Whereas fossil fuel combustion is the main source of CO at Northern mid-latitudes, the oxidation of isoprene and biomass burning play an important role in the tropics. TROPOMI on ESA's Sentinel 5 Precursor (S5P) satellite observes the CO global abundance exploiting clear-sky and cloudy-sky Earth radiance measurements in the 2.3 µm spectral range of the shortwave infrared (SWIR) part of the solar spectrum. TROPOMI clear sky observations provide CO total columns with sensitivity to the tropospheric boundary layer. For cloudy atmospheres, the column sensitivity changes according to the light path. The figure below shows the S5P/TROPOMI CO total column mixing ratio averaged from November 13th to 19th, 2017 (from Borsdorff et al., GRL 2018). The data show clearly CO enhancements by wildfires in Brazil, Africa, Madagascar, and Australia as well as anthropogenic air pollution in India and China.Layer ID: ID: AWS_VIS_CO_3DAILY_DATA collectionID: 57a07405-8ec2-4b9c-a273-23e287c173f8 from 20180430 - ongoingBand information
The product contains one single band named "co".More information
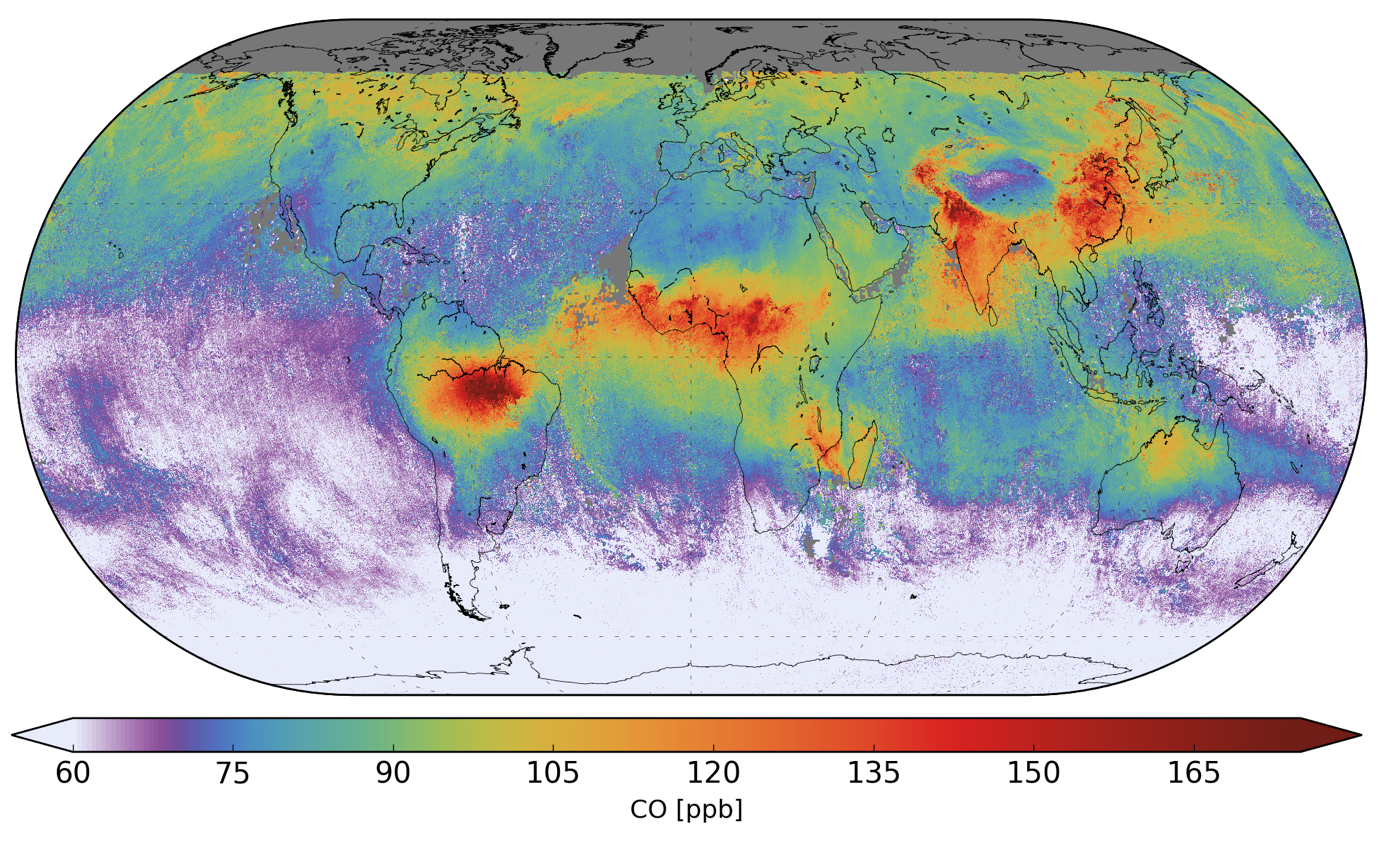
S5P/TROPOMI CO total column mixing ratio averaged from November 13th to 19th, 2017 (from Borsdorff et al., GRL 2018). The data show clearly CO enhancements by wildfires in Brazil, Africa, Madagascar, and Australia as well as anthropogenic air pollution in India and China.